15 Types of Sudoku: How to Solve Different Variants
Sudoku has become one of the most popular logic puzzles in the world, but what many players don’t realize is that you have more than one way to play. Beyond the classic Sudoku puzzle, dozens of Sudoku variations have emerged, each with unique rules, layouts, and levels of challenge.
Some versions of Sudoku keep the familiar 9×9 grid but layer on new rules, add in arithmetic, or use visual imagery to adjust how you solve the puzzle. To help demystify all the differences, this guide walks you through 15 different types of Sudoku, grouped by puzzle style.
Whether you’re a beginner learning the Sudoku rules or an advanced solver looking for your next online Sudoku challenge, you’ll find a version of Sudoku that matches your interests and skill level. Just use this handy chart as a quick reference or dig deeper in the post for more how-to-play details for each version.
| Type of Sudoku | Grid Style | Unique Twist | Level of Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini | 4x4 or 6x6 | The puzzle uses a smaller grid. | Beginner |
| Classic | 9x9 | The grid follows standard Sudoku rules. | Varies from easy to evil |
| Super/Giant | 16x16 or larger | This puzzle uses oversized grids. | Advanced |
| Jigsaw | 9x9 with odd-shaped regions | 3x3 blocks are replaced with uniquely shaped regions. | Intermediate |
| Samurai | Five overlapping 9x9 grids | You must solve multiple grids. | Advanced |
| Windoku | 9x9 grid with extra regions | Extra regions must follow standard rules. | Intermediate |
| Sudoku X | 9x9 grid with diagonals | Digits must also appear once along diagonals. | Intermediate |
| Skyscraper | 9x9 grid with outside clues | Outside numbers show how many skyscrapers are visible from each side of a row or column. | Advanced |
| Killer | 9x9 grid with cages | Digits in a cage must add up to the given total. | Advanced |
| Even-Odd | 9x9 grid with shaded cells | Shaded cells are restricted to even/odd numbers | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Consecutive | 9x9 grid with marked dots | Adjacent cells must be consecutive digits. | Intermediate |
| Greater-Than | 9x9 grid with inequality signs | Cells must respect the inequality clues. | Intermediate |
| Arrow | 9x9 grid with arrows | Digits in the arrow must add up to the circle's value. | Advanced |
| Wordoku | 9x9 grid with letters | Numbers are replaced with letters. | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Color | 9x9 grid with colors | Numbers are replaced with colors. | Beginner to Intermediate |
Classic and Size-Based Sudoku
Classic Sudoku is what you typically think of as a normal Sudoku puzzle: a 9×9 grid. But some types of Sudoku are smaller or larger (much larger!) than the standard 9×9. However, these size-based versions all follow the standard Sudoku rules where each row, column, and 3×3 block contains the digits 1 through 9 without repeats.
The classic version makes a great entry point for Sudoku. After you gain confidence working normal Sudoku puzzles, you can move on to puzzles that layer more constraints, add more rules, or change the rules completely.
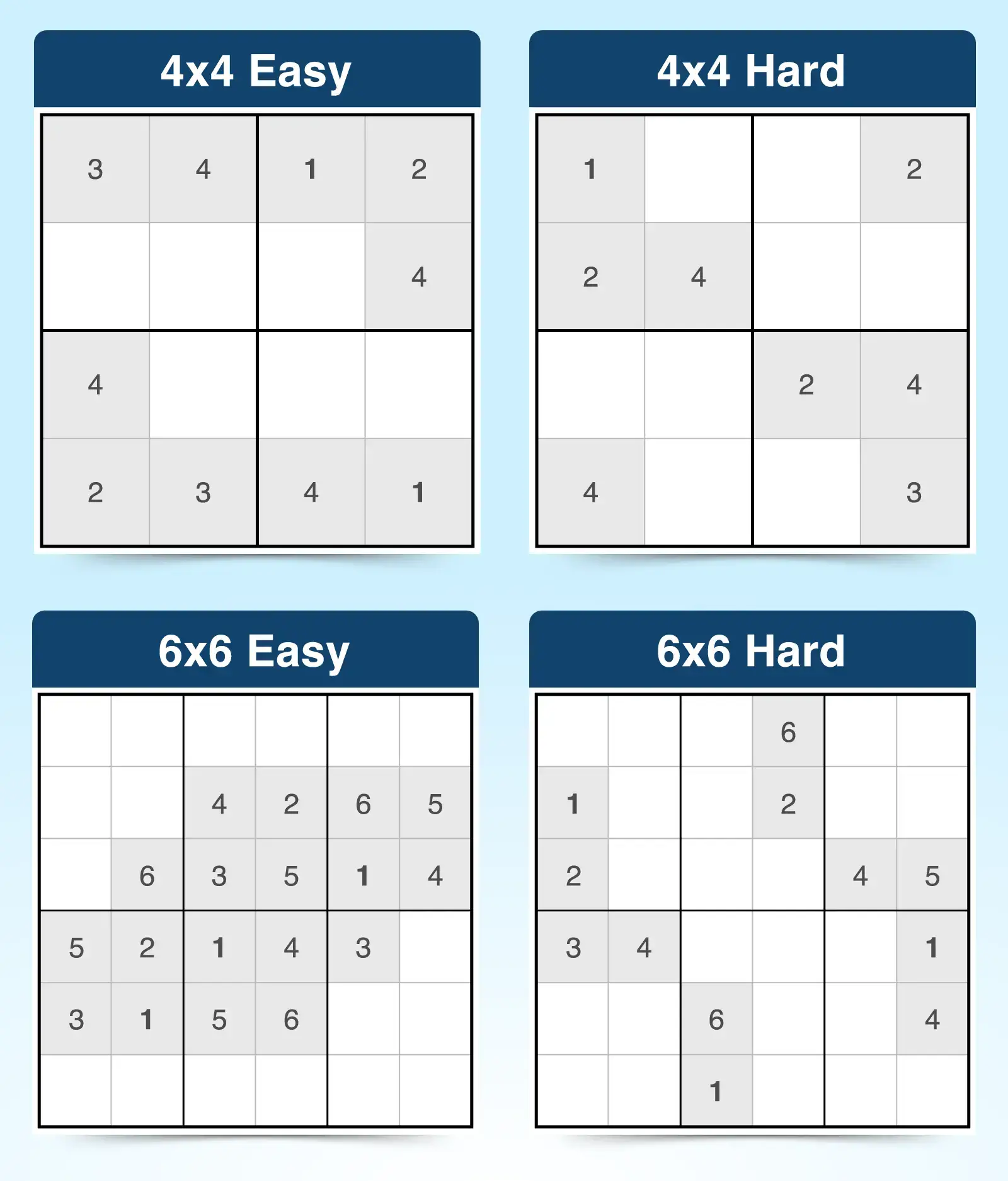
1. Mini Sudoku
Mini Sudoku makes for a great entry-level Sudoku puzzle for kids. The grid is only 4×4 or 6×6 and comes in easy and hard varieties. It follows the same Sudoku rules but you only use numbers 1 through 4 or 1 through 6, depending on the size of the grid.
2. Classic Sudoku
With a familiar-looking 9×9 grid pattern, these puzzles follow standard Sudoku rules, and you can find them in a variety of difficulty levels to suit a wide range of solving skills.
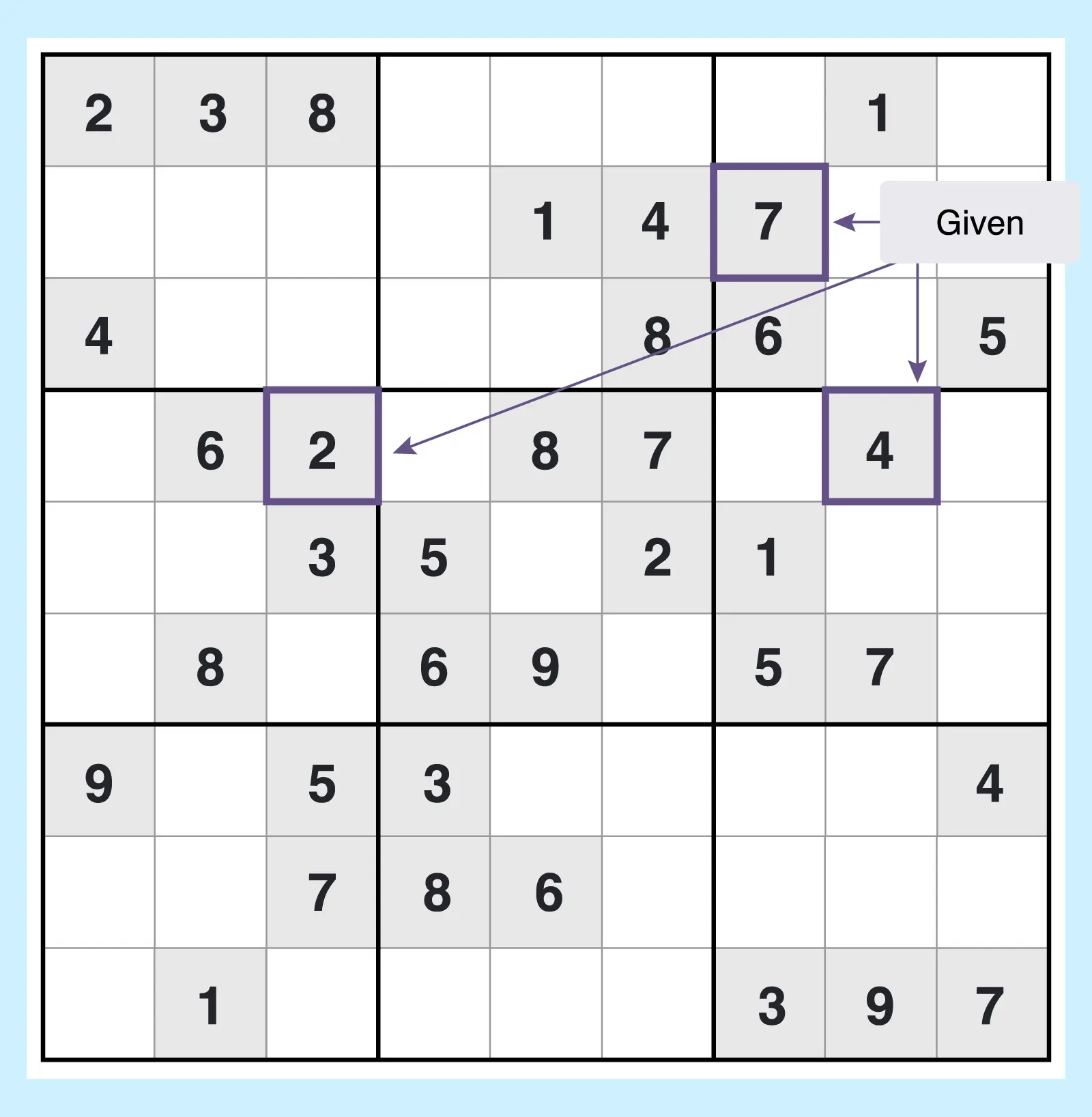
The difficulty ranges from easy to evil, depending on which level you choose, and as you move up each level, the number of given digits (answers already present in the grid) become fewer and fewer.
- Easy: If you’re just learning how to play Sudoku, easy puzzles provide the best opportunity to learn the rules and use basic techniques, like scanning.
- Medium: As you step up a level in difficulty, these puzzles help you add to your solving skills, using techniques, such as naked pairs and the last possible candidate.
- Hard: When you reach this level, you’ll need to take advantage of a wide range of Sudoku techniques to solve these challenging puzzles.
- Expert: Offering even fewer givens than hard puzzles, these Sudoku grids require you to use even more techniques, such as XY-wing and unique rectangle.
- Evil: Just as the name suggests, these villainous puzzles will have you using advanced skills to crack these difficult puzzles.
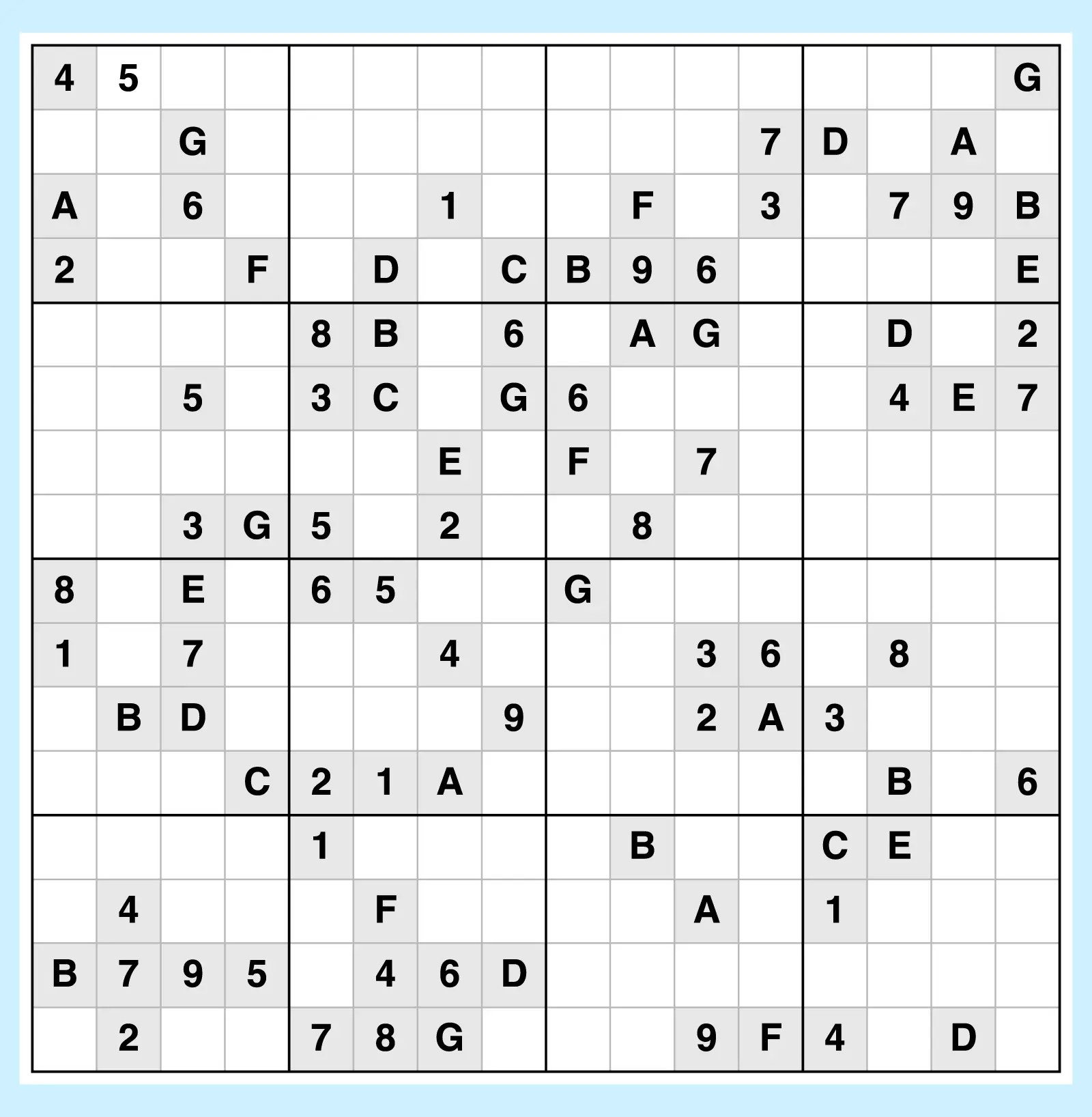
3. Super/Giant Sudoku
These 16×16 puzzles (or larger!) expand the classic 9×9 grid into an oversized challenge. Solvers must apply the same Sudoku solving strategies, but on a much larger scale.
Shape and Grid Variants
These versions of Sudoku twist the familiar puzzle type by changing the shape of the units (rows, columns, and blocks) or by combining multiple grids. They look familiar, but you’ll discover they play very differently from standard Sudoku, although you can often still use many of the basic Sudoku techniques for solving.
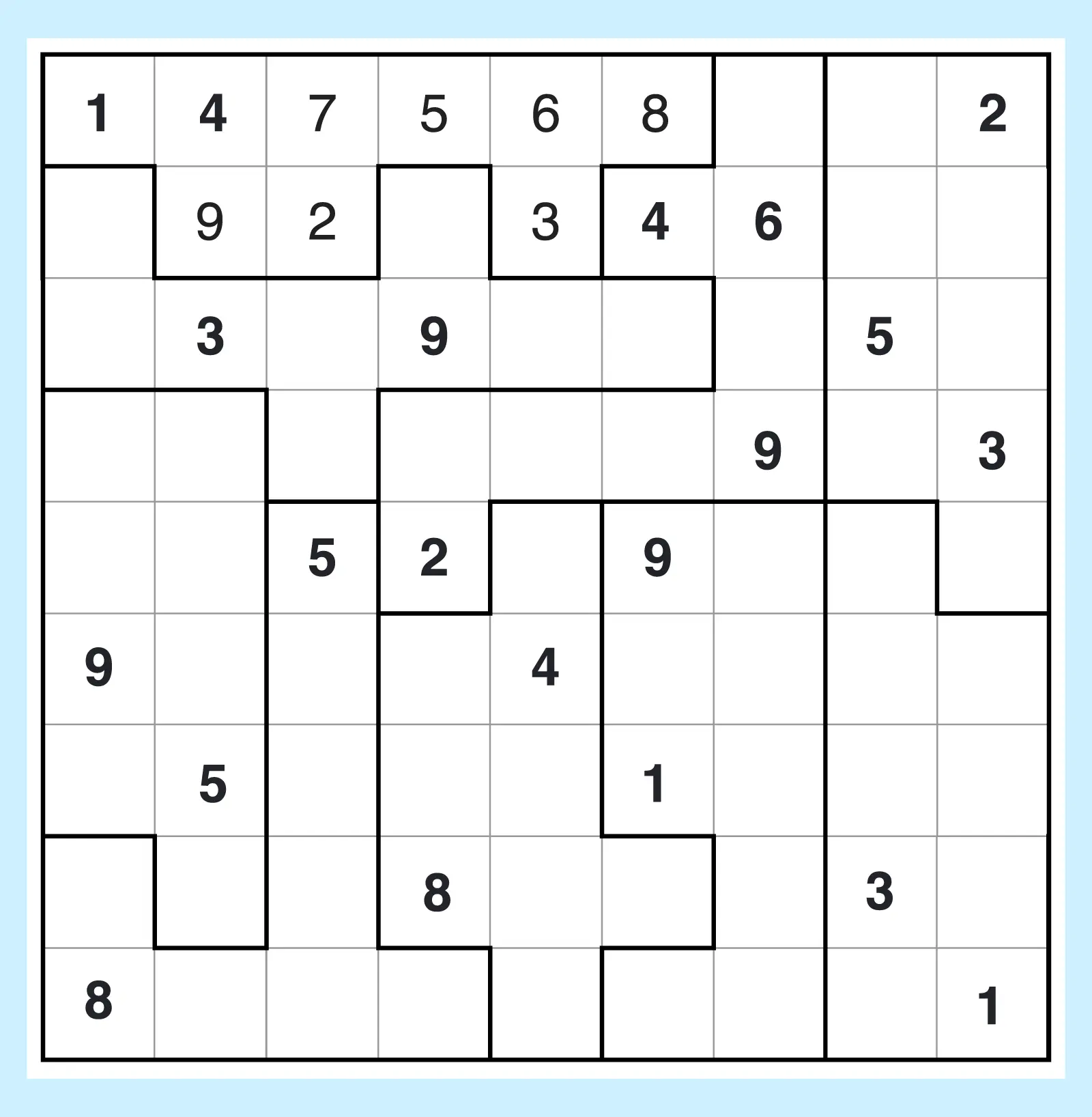
4. Jigsaw Sudoku
Instead of square blocks, jigsaw Sudoku (also called irregular Sudoku) uses odd-shaped regions. You still must place the same numbers 1 to 9 in each row and column, but instead of a uniform block layout, you have to also place the numbers, with no repeats, inside of each puzzle-looking piece. This version plays just like classic Sudoku with nine puzzle pieces replacing the blocks.
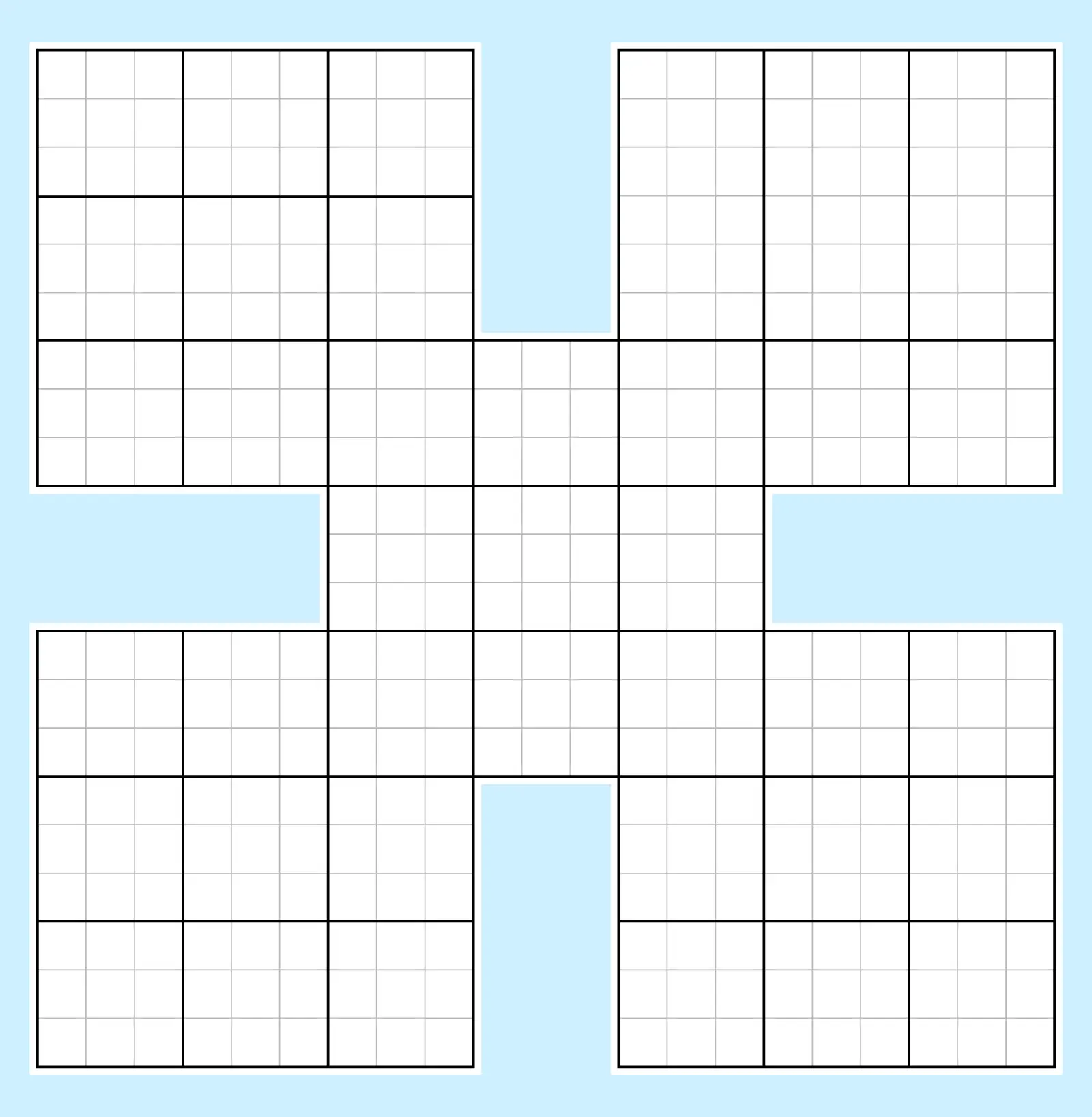
5. Samurai Sudoku (Gattai Sudoku)
Also called Gattai, this Sudoku variant uses five overlapping 9×9 grids arranged in an X shape. Samurai Sudoku puzzles can take much longer to solve and are best tackled by advanced solvers.
The overlapping corners of the middle grid gives you another point of restriction that allows you to compare units and candidates, but the sheer number of grids you must solve simultaneously adds to the challenge. Use advanced strategies on the individual blocks for the best chance of success with these puzzles.
Rule-Based Sudoku Variants
These Sudoku variations add extra rules on top of the classic 9×9 grid, creating fresh challenges for experienced solvers.
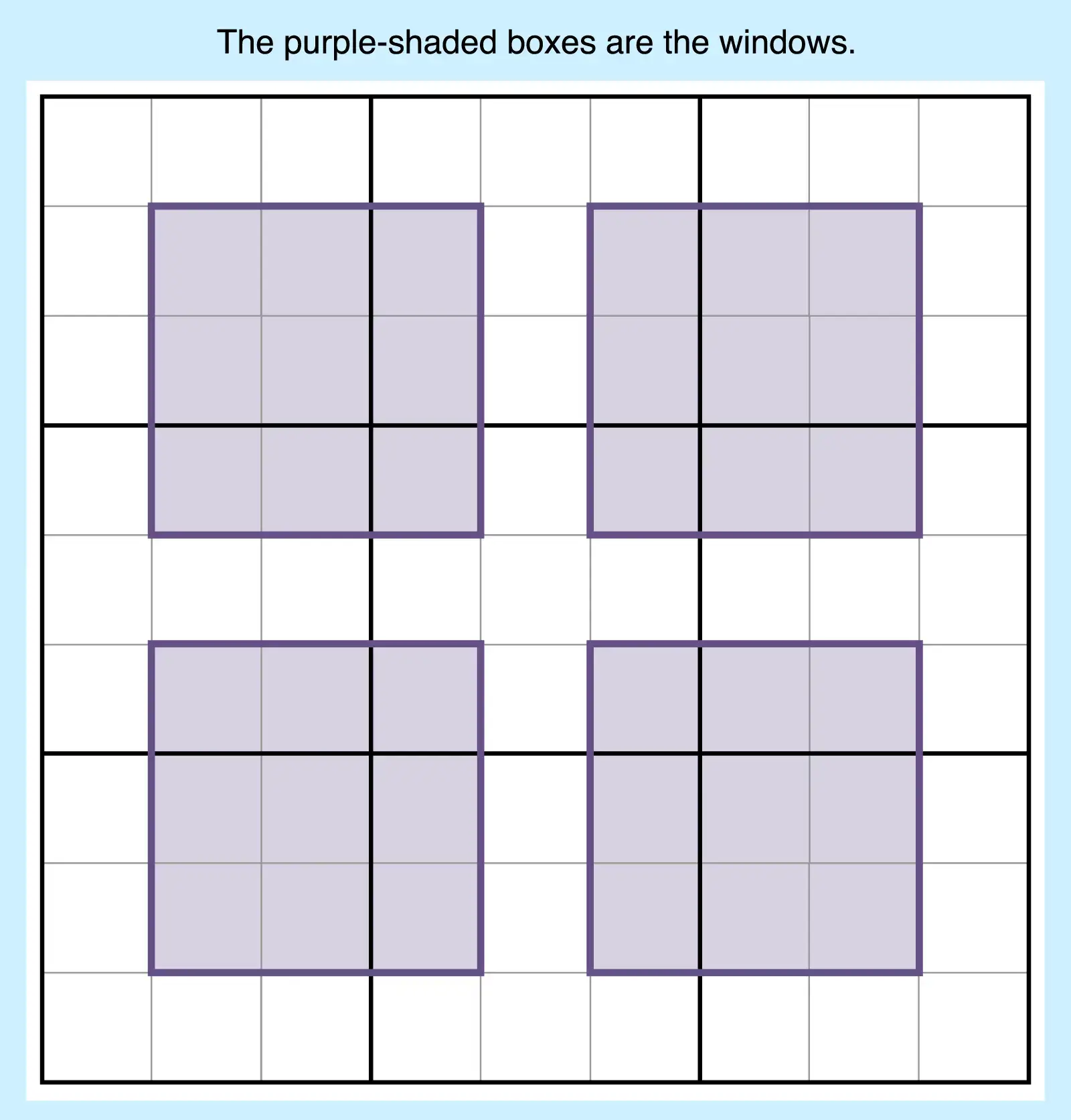
6. Windoku
This version of Sudoku, which is also called hyper Sudoku, adds four extra shaded 3×3 regions within the grid, like windows. Numbers 1 to 9 must appear in these areas, too, increasing difficulty beyond normal Sudoku. However, because these shaded areas restrict possible candidates, they help narrow the possibilities.
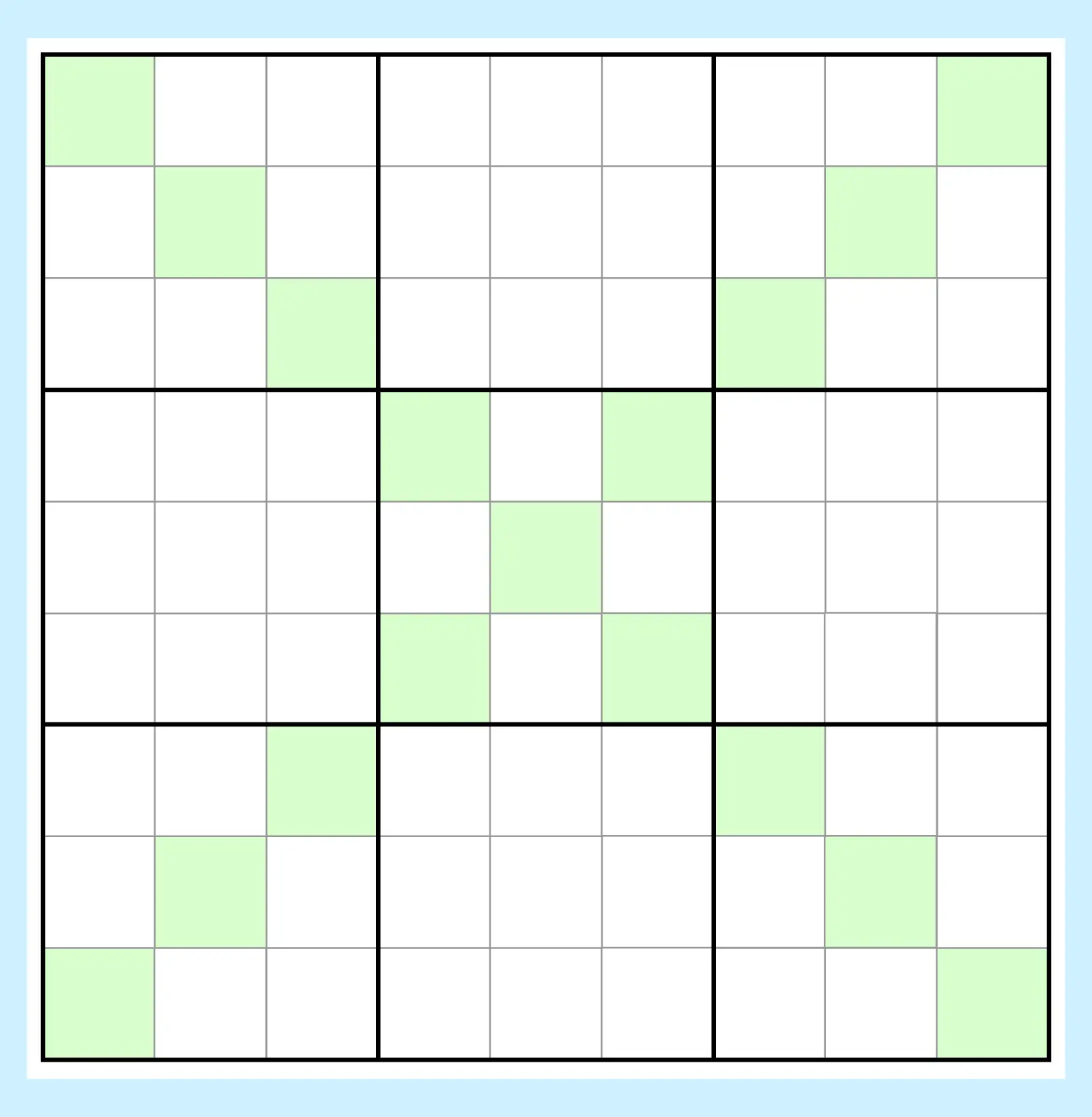
7. Sudoku X (Diagonal Sudoku)
Known as Sudoku X or X-Sudoku, this variant requires digits 1 to 9 to also appear once along both main diagonals of the 9×9 grid. The crossing diagonal lines create an extra layer of constraint that adds complexity to candidate placement.
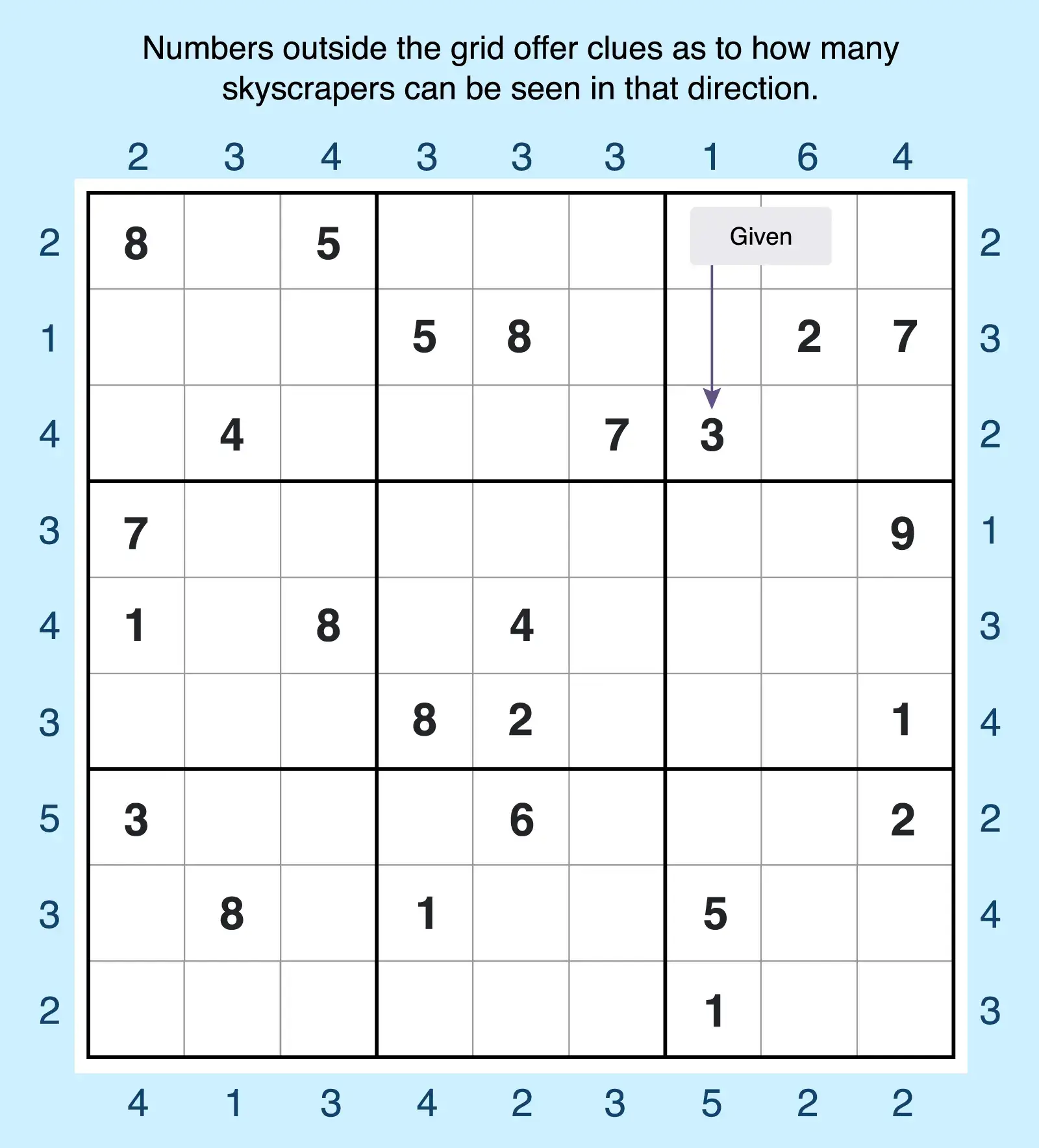
8. Skyscraper Sudoku
In Skyscraper Sudoku, the numbers in each cell of the 9x9 grid represent the height of skyscrapers. Clues outside the grid tell you how many skyscrapers are “visible” in that row or column, following the same logic as visibility puzzles. The tallest numbers block the smaller ones behind them. This adds a spatial, visual twist to Sudoku solving, blending classic Sudoku rules with the mechanics of other logic puzzles.
9. Killer Sudoku
This puzzle type combines Sudoku with arithmetic. Numbers must obey the standard Sudoku rules for placement, but the digits within outlined cages must also add up to the sum contained in the cage. This makes Killer Sudoku one of the hardest and most rewarding logic puzzles.
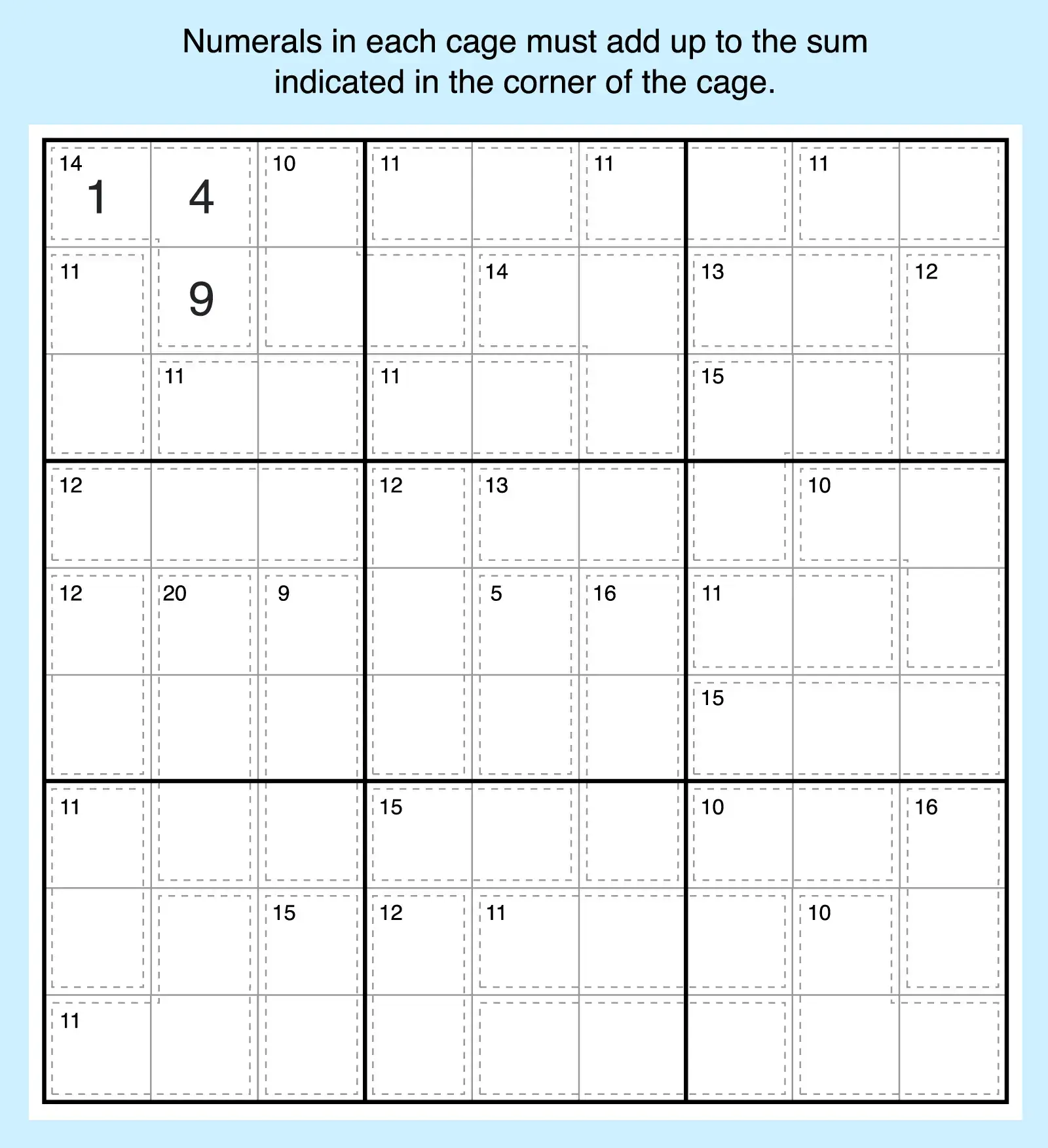
Math-Based Sudoku Variations
Some Sudoku variations go beyond simple placement rules by adding arithmetic into the mix. These puzzles require solvers to use consecutive digits, calculate sums, compare values with inequality signs, or apply even-odd restrictions while still following the standard Sudoku rules. Math-based Sudoku puzzles add an extra layer of challenge and are popular among players who enjoy combining number theory with logical reasoning.
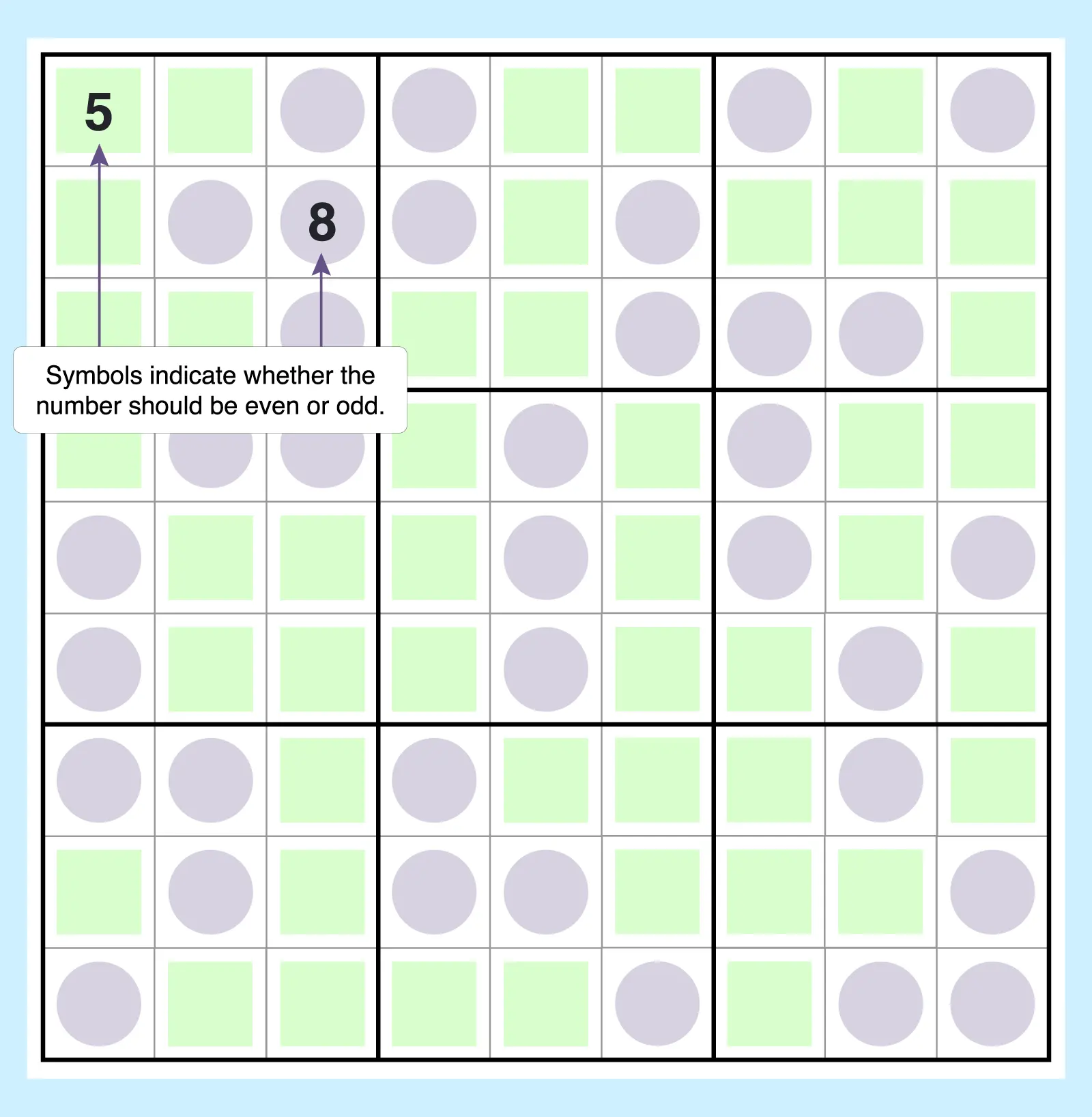
10. Even-Odd Sudoku
Some cells are shaded to require even or odd numbers only. This simple rule dramatically shifts how solvers approach candidate elimination compared to standard Sudoku. After you narrow down candidates, you can narrow down further by evens or odds.
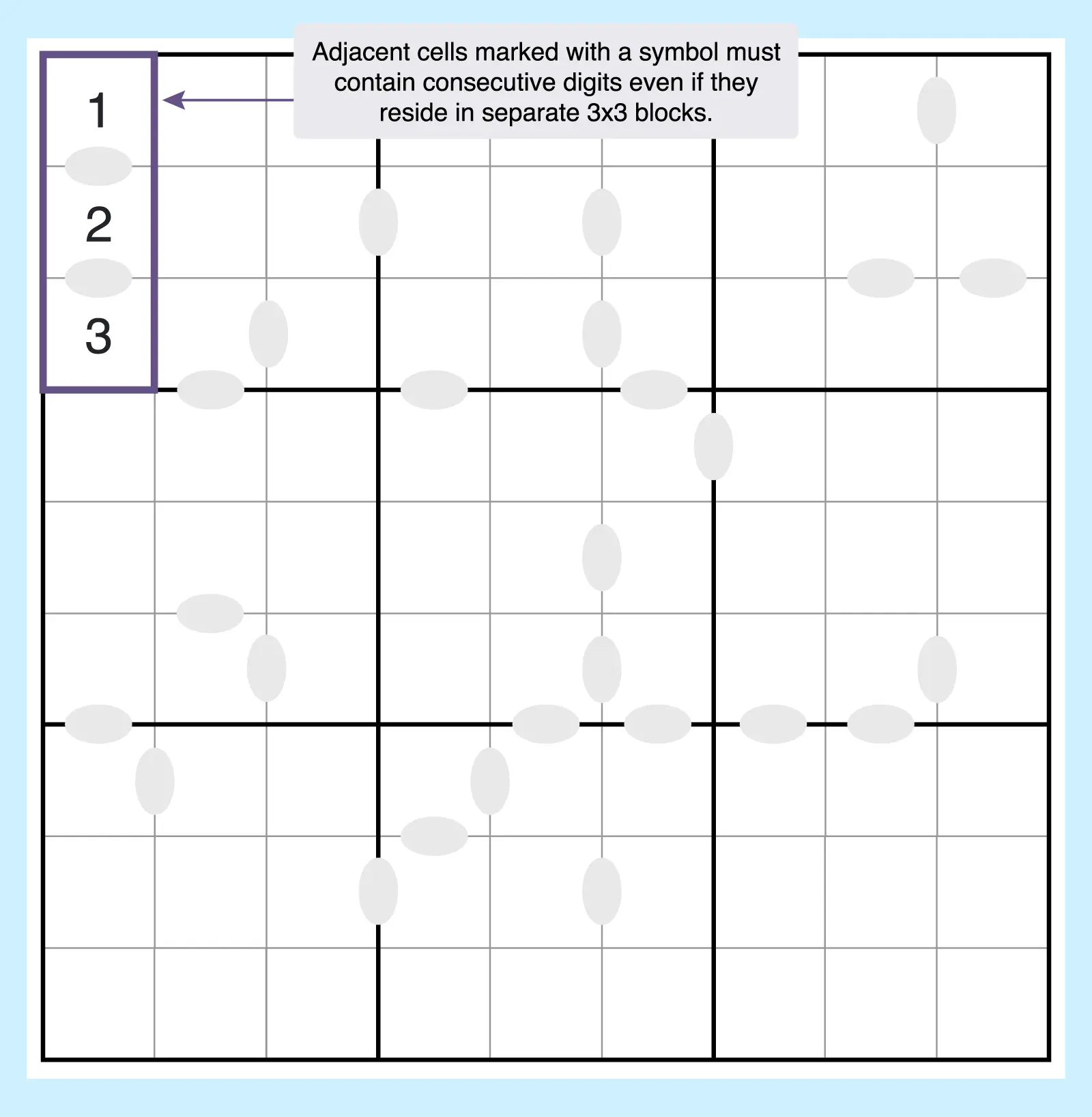
11. Consecutive Sudoku
In this Sudoku version, adjacent cells marked with a symbol must contain consecutive digits. In non-consecutive versions, no two adjacent cells may contain consecutive numbers. Both add new twists to traditional Sudoku solving.
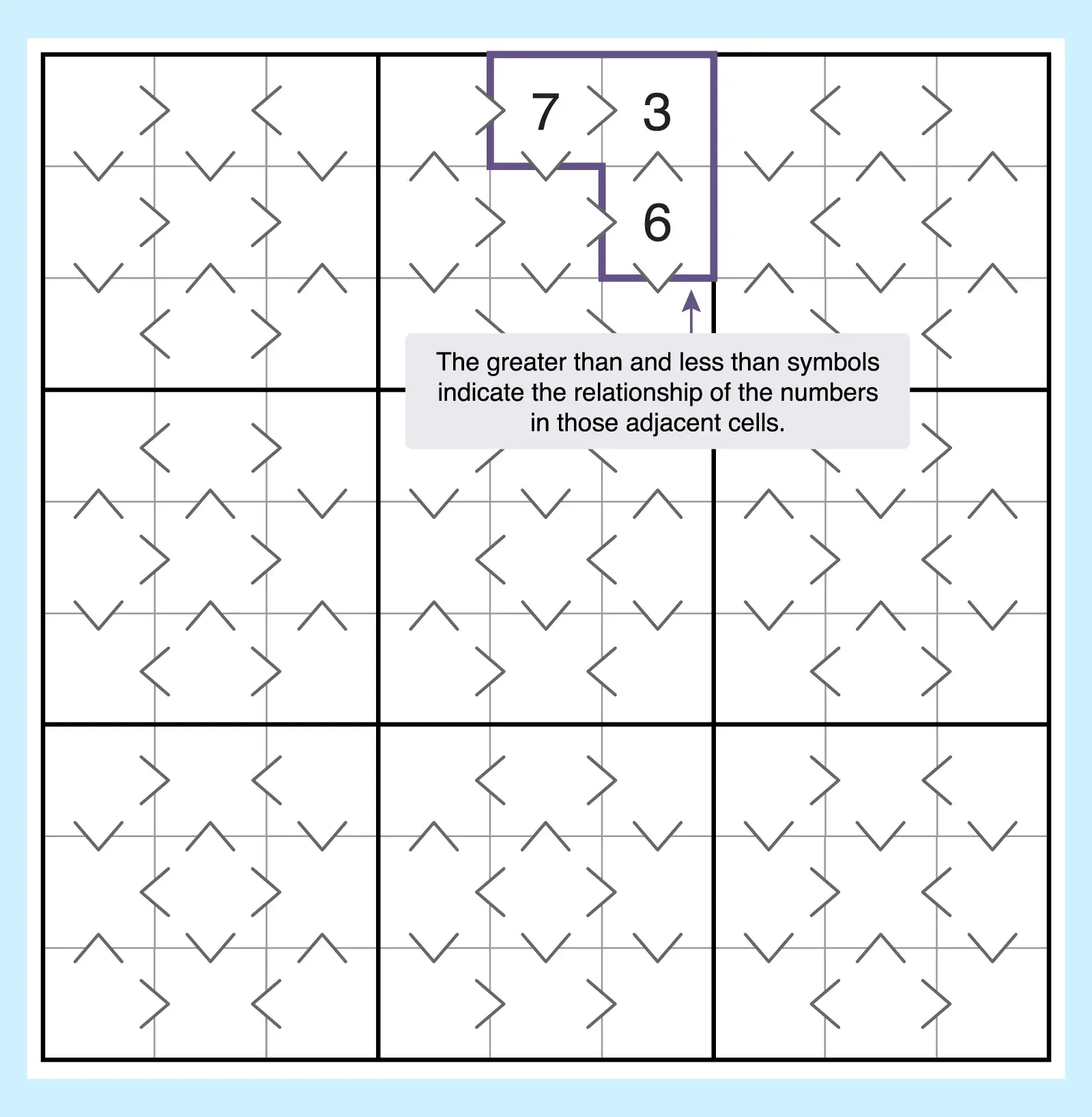
12. Greater-Than Sudoku
Sometimes called Inequality Sudoku, this puzzle places comparison signs ( < or > ) between cells. Solvers must respect both the Sudoku rules and the inequality clues. This offers another clue to eliminate possible candidates in cells.
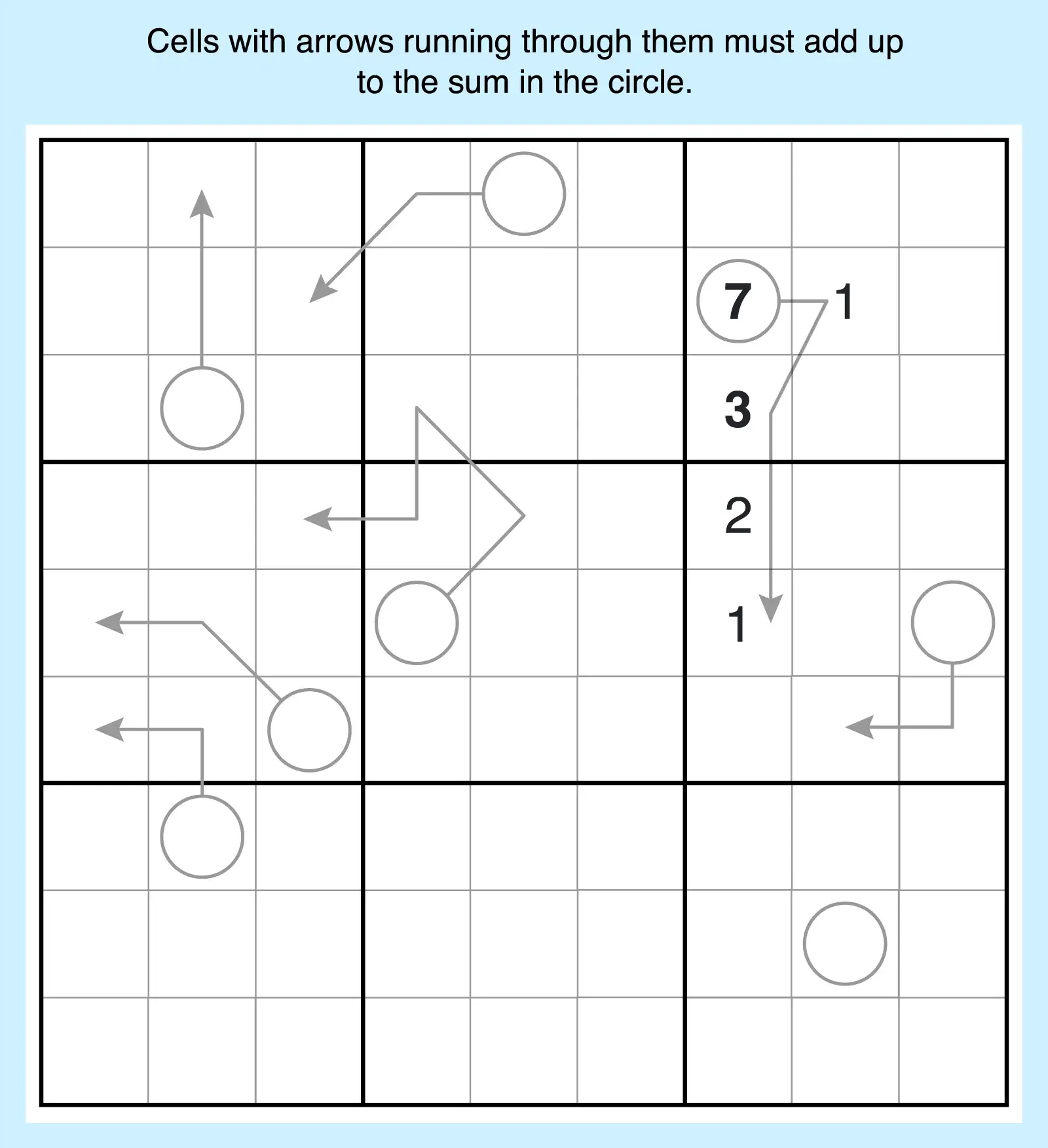
13. Arrow Sudoku
In Arrow Sudoku, the numbers along each arrow must add up to the total in the circle at its base. This adds a layer of arithmetic similar to killer Sudoku that helps you narrow down possible candidates for cells by determining whether they can be part of the mathematical equation.
Visual Variants
These Sudoku puzzles replace numbers with letters, words, shapes, or colors. The rules stay the same, but the look and theme make them accessible to different skill levels.
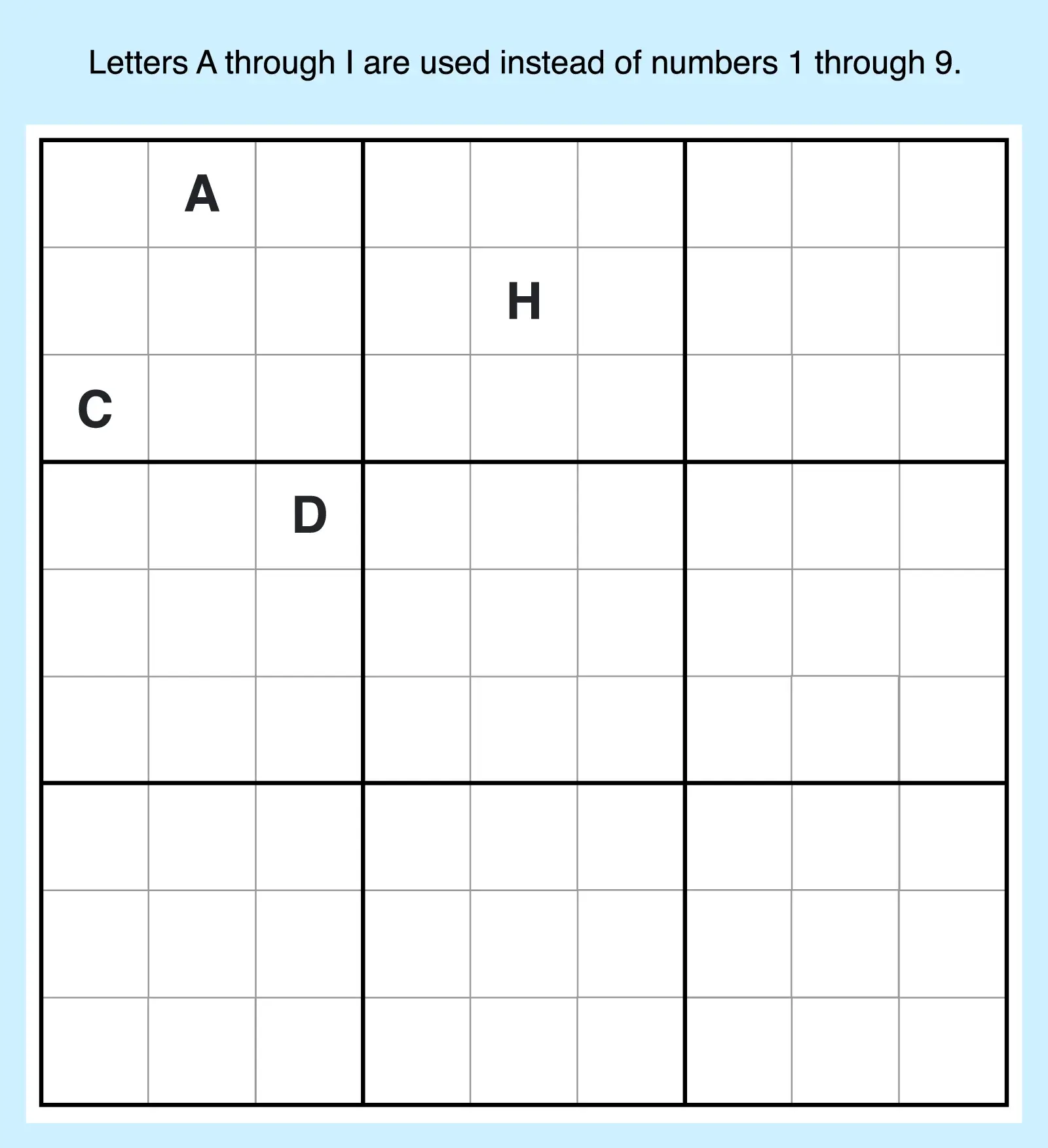
14. Wordoku
Instead of digits, Wordoku uses letters A through I in a 9×9 grid. Sometimes the letters spell a hidden word, adding a fun extra challenge to this puzzle type.
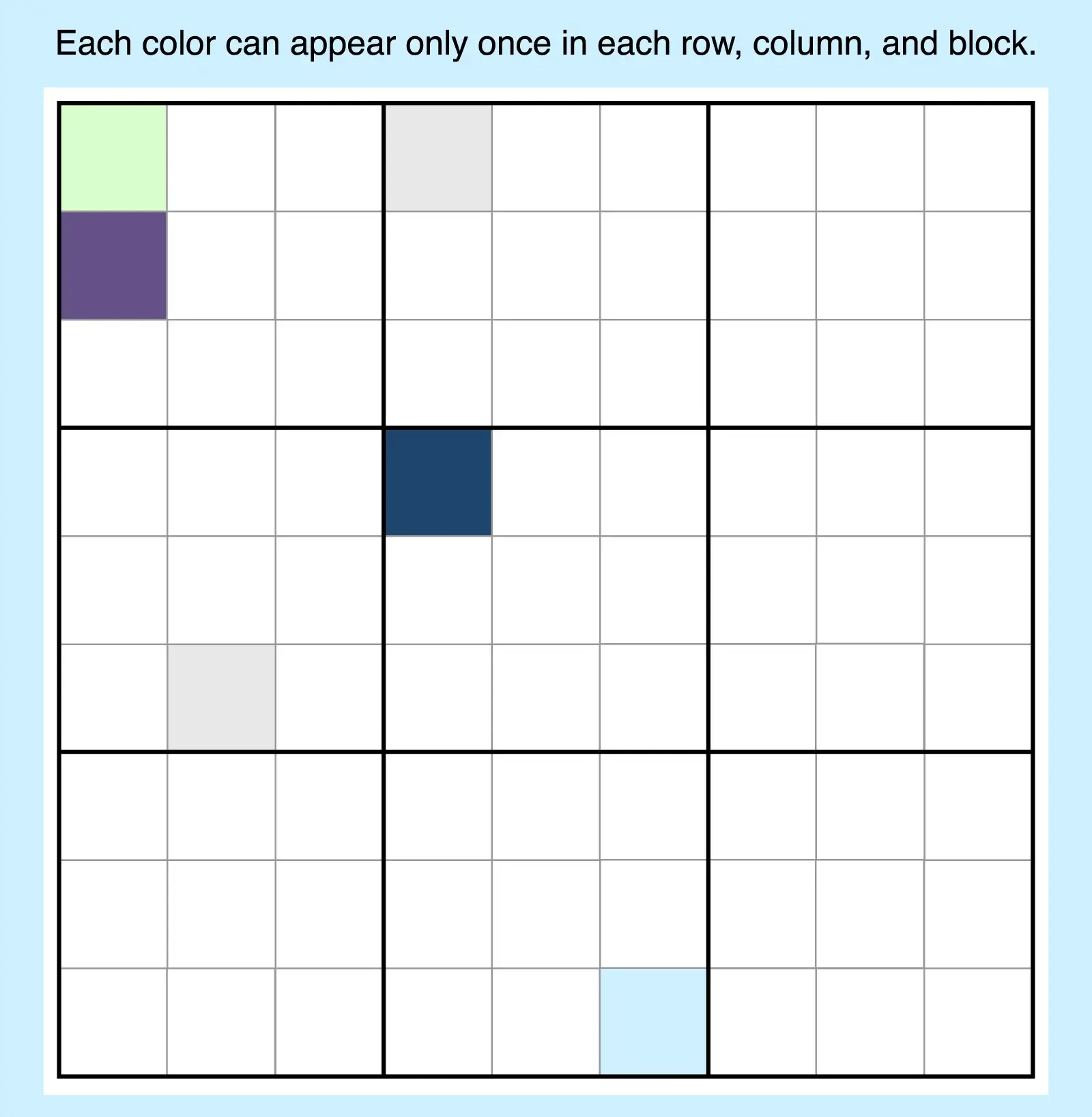
15. Color Sudoku
Instead of numbers, solvers place colors, symbols, or pictures. This makes the puzzle more approachable for kids and those new to Sudoku variations, but the logic puzzle structure remains the same.
How to Choose the Right Sudoku for You
With so many different types of Sudoku, you can pick puzzles based on your skill level, mood, and preferences. Whether you’re browsing online Sudoku puzzles or flipping through puzzle books, use these tips to pick the right puzzle type:
- Start with classic Sudoku if you’re new to the game. If Sudoku is a new adventure, stick with the standard 9×9 grid. It’s the best way to learn the Sudoku rules and build confidence.
- Pick the right skill level. You can choose from a variety of levels in classic Sudoku, but different types of Sudoku offer even more puzzling adventures at different levels of difficulty. Beginners can try mini Sudoku or Wordoku for faster solving while those at a medium or intermediate level should move to diagonal Sudoku (Sudoku X) or jigsaw Sudoku to stretch your logic. For the more advanced, challenge yourself with samurai Sudoku (Gattai), killer Sudoku, or skyscraper for complex multi-layer solving.
- Consider your time commitment. If you’re short on time, a mini Sudoku or easier version is a perfect choice. But if you want a marathon Sudoku session, picks like samurai may be a better choice.
- Pick by puzzle style. You can always count on classic Sudoku to scratch your puzzling itch, but if you like math, killer Sudoku and arrow versions get you calculating quickly. On the other hand, if you prefer patterns or something more visual, Windoku or color Sudoku offer a mix of imagery and spatial logic.
With so many different types of Sudoku, you can always find a new puzzle to match your mood, skill level, or time commitment. Whether you’re just learning how to play Sudoku or learning advanced sudoku strategies, you can explore and play a wide variety of Sudoku puzzles online today and see which version of Sudoku challenges you the most.